这篇文章是我的个人实践经验:
很多朋友在做Proteus硬件仿真的时候可能都碰上了仿真速度慢的问题,在点击了开始仿真之后,CPU过载,速度极慢,无法正常进行仿真;Proteus在信息栏提示CPU被使用情况,可能高达90%到100%,并没有按照真实速度仿真,点击信息栏中的提示信息就弹出一个对话框,说是 Simulation is not running in real time due to excessive CPUload,鼠标点击提示,会展开一个消息框,下面就是消息框内的内容:
This message has been generated because the simulation has been unable to keep up with real time for more than 20 consecutive simulation frames. This does not affect the accuracy of the simulation in any way, but it will mean that the simulated system may respond much more slowly to interactive events(e.g. push buttons).
See Also:
How to make simulations run faster?
这里的说明中可以看到至少两个信息:第一,速度慢并不影响仿真精度;第二,我们可以点击最下方那句话打开另一个链接来加速仿真;那么,我们就继续按照提示来寻找答案。(也许我们的Proteus版本不同,这些链接打开顺序和方法可能不一样,我是用的是7.1的版本)点击 How to make simulations run faster?打开Proteus的帮助,进入一个英文界面,我把原文全部贴在这里,之后和你一起解读。
ADVANCED TOPICS
HOW TO MAKE INTERACTIVE SIMULATIONS RUN FASTER
Introduction
Although Proteus VSM is able to run many interactive simulations in real
time, it should be fairly obvious that this cannot be the case for all
circuits. For example, it is perfectly possible to draw a circuit that will
oscillate at 1GHz, but there is no way that this can be simulated in real
time on a computer that may not even execute one machine instruction in 1ns.
In this section, we will explain in a little more detail what determines the
complexity of a simulation and how you can optimize a circuit to maximize the
simulation speed.
Using Digital Resistor and Diode Models
First and foremost in this context, it is vital to understand the difference
between analogue and digital simulation within ProSPICE. This is because the
simulation of digital circuitry is two or three orders of magnitude (i.e. up
to 1000 times) faster than the simulation of analogue circuitry. It is for
this reason that ProSPICE contains a digital simulator at all - that by
representing the operation of digital components as an event driven process,
a great deal of unnecessary computation can be avoided.
For example, whilst a PC with 600MHz P3 processor can simulate around 2
million digital events per second, the same computer will only be able to
simulate a sine wave generator running up to about 2kHz before the CPU load
reaches 100%. Such a waveform will require about 60,000 analogue timepoints
to be computed per second, and each timepoint will require a convergent
solution of the circuit nodal equations to be established - a process vastly
more complex than processing a simple digital event.
For many components, it should be fairly intuitive as to whether analogue or
digital simulation will be required. For example, nearly all TTL and CMOS
parts are represented by digital models, whereas analogue ICs such as op-
amps, comparators and so forth are represented by analogue models. All
components which are represented by standard SPICE models require analogue
simulation.
However, a grey area arises for components which - though strictly analogue
in nature - can be represented by a digital model for some purposes. In
particular, diodes - and perhaps more surprisingly - resistors fall into this
category. This becomes highly relevant in the context of wire-or logic, pull
-up resistors, devices with open-collector outputs, and in diode-resistor
logic networks.
Example 1 - Wire-Or Logic
The following circuit section shows a typical wire-or logic network:

U1:A and U1:B have open-collector outputs and can only sink current. A logic
1 output level results in a high impedance condition. In terms of DSIM, this
means that the gate outputs drive either an SLO (strong low) or a FLT
(floating) logic state. Now if resistor R1 is modelled in the analogue
domain, PROSPICE must insert a digital to analogue interface object between
the logic gates and the resistor, and then an analogue to digital interface
object between the resistor and the input to U2:A. This will result in
wonderfully detailed simulation of the rise-fall waveforms at this node, and
the current flow through R1, but will also result in a great deal of
computation every time the output of U1:A or U1:B changes state.
All this can be avoided if R1 is modelled digitally. In this case, its
behaviour is to convert the SHI logic state of VCC to a WHI (weak high) logic
level. When either NAND gate pulls low, the SLO state overrides the WHI state
from the resistor and the net state is resolved to be logic low. But when
neither gate sinks current, the WHI state beats the FLT state and the net
rises to logic high. All this can be managed within the digital simulation
paradigm and no analogue simulation is required.
Therefore, pull up resistors of any kind should almost always be modelled
digitally.
Example 2 - Diode-Resistor Logic
Another case where seemingly analogue circuitry can be modelled in the
digital domain is diode-resistor networks of the sort shown below. These are
often found around keypad scanning circuitry where the diodes serve to
prevent short circuits between the row driving lines if more than more than
one key is depressed simultaneously.
As with the wire-or logic example, ProSPICE will quite happily model this in
the analogue domain but it will be computationally expensive. If a digital
resistor model is used as above, and a diode is seen as a device which will
pass only low logic level from cathode to anode and only a high logic level
from anode to cathode, then the whole network can once again be modelled
digitally.
Since keypad scanning routines tend to operate at some speed, and there are
often numerous diodes and resistors, this is a very important optimization to
be aware of.
How to Select the Digital Resistor Model
1. Point at the resistor you wish to change and press CTRL-E.
2. Click the Edit All Properties as Text checkbox.
3. Change the PRIMITIVE property to read
PRIMITIVE=DIGITAL,RESISTOR
If you are building a circuit from scratch, and know that you will want a
particular resistor to be modelled digitally, you can also achieve this by
picking the PULLUP or PULLDOWN models from the component library. This
devices already contains the PRIMITIVE property as above.
How to Select the Digital Diode Model
1. Point at the diode you wish to change and press CTRL-E.
2. Click the Edit All Properties as Text checkbox.
3. Change the PRIMITIVE property to read
PRIMITIVE=DIGITAL,DIODE
4. Delete any MODEL property, as SPICE parameters have no meaning for the
digital diode model.
If you are building a circuit from scratch, and know that you will want a
particular diode to be modelled digitally, you can also achieve this by
picking the DIODE-DIGITAL device the component library. This device already
contains the PRIMITIVE property as above.
Optimizing Memory Accesses to External RAM and ROM
Many larger microprocessor designs make use of ROM, RAM or EEPROM memory
devices external to the microcontroller itself. These may store the program
code, or be used to supplement internal SRAM present within the CPU chip
itself. Given a correct address decoding circuit, and assuming that the
memory device is modelled, Proteus VSM will correctly simulate such designs
as drawn. When the CPU accesses external memory, the model will drive the
address, data and control lines appropriately, and external decode logic and
memory model will respond by reading or writing the appropriate locations.
This is quite useful if you wish to verify that your memory decoding
circuitry works as designed, but is also extremely expensive in terms of
computation. Setting up a 16 bit address will create a minimum of 16 digital
events and reading or writing a byte of data to/from data bus will generate
another 8. Removing the data from the bus afterwards will create another 8
events. Where address and data lines are multiplexed, as in the above HC11
design, even more events will be generated. All this compares very
unfavourably with the ability of a VSM CPU model to execute an instruction
using just one event per machine cycle.
Therefore, we have provided the CPU models with the ability to simulate
accesses to external memory internally to the model. At the time of writing
this applies to the 8051,
HC11 and the larger AVR CPU models. External memory may be declared using
EXTRAM, or EXTROM properties which specify the memory range for each block of
external memory. Full details are provided in the model specific help for
these processors, which you can access from the Edit Component dialogue form,
or from the Start Menu.
Once the external memory map has been defined in this way, instructions which
access external memory within the specified ranges can be simulated without
generating large numbers of digital events. Accesses to memory mapped
peripherals can still be fully simulated, since these will lie at locations
outside the memory ranges specified in the EXTRAM and EXTROM properties.
这里就列出了所有问题的根源了;各位朋友不妨多看看这里的英文帮助,磨刀不误砍柴
工,这里的帮助内容比任何人的经验之谈要高明得多;
好了,让我来读读这里的帮助,下面是我读出的基本内容之一:
第一:使用数字式的电阻和二极管(Using Digital Resistor and Diode Models)
这句话是我的翻译,原文的意思是如果把所有的二极管和电阻都看成是模拟量那样仿真的话,Proteus的速度会大大下降;所以所有的上拉电阻都可以看成是数字量的模拟(原文是:Therefore, pull up resistors of any kind should almost always bemodelled digitally.);而一些作为逻辑门电路用的二极管也可以看成数字式的;因此,需要对仿真的元件进行设置。
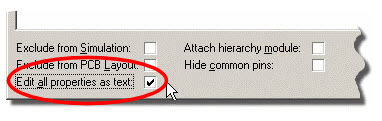
1)对电阻的设置(How to Select the Digital Resistor Model) How to Select the Digital Resistor Model
1. Point at the resistor you wish to change and press CTRL-E.
2. Click the Edit All Properties as Text checkbox.
3. Change the PRIMITIVE property to read
PRIMITIVE=DIGITAL,RESISTOR
2)对二极管的设置(How to Select the Digital Diode Model)
1. Point at the diode you wish to change and press CTRL-E.
2. Click the Edit All Properties as Text checkbox.
3. Change the PRIMITIVE property to read
PRIMITIVE=DIGITAL,DIODE
4. Delete any MODEL property, as SPICE parameters have no meaning for thedigital diode model
另外说明,在编辑Properties时,在文本框里键入的内容若用中括号{}括起来,那么在仿真界面就不会显示出来,比如
{MODFILE=74AND2.MDF}
{PACKAGE=DIL14}
{ITFMOD=TTL}
第二:Optimizing Memory Accesses to External RAM and ROM
这个问题我还没有遇到过,也不太明白其中的内容,希望比较熟悉单片机方面有的朋友做补充了!!!

 U澶у笀v4.7.37.56 鏈€鏂扮増
U澶у笀v4.7.37.56 鏈€鏂扮増 HD Tune Prov5.75 姹夊寲缁胯壊鐗瑰埆鐗�
HD Tune Prov5.75 姹夊寲缁胯壊鐗瑰埆鐗� DiskGenius 涓撲笟鐗圴5.2.1.941 瀹樻柟鐗�
DiskGenius 涓撲笟鐗圴5.2.1.941 瀹樻柟鐗� 360杞欢绠″v7.5.0.1460 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
360杞欢绠″v7.5.0.1460 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 Cpu-Z涓枃鐗坴1.98.0 缁胯壊涓枃鐗�
Cpu-Z涓枃鐗坴1.98.0 缁胯壊涓枃鐗� 鑵捐鐢佃剳绠″V15.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
鑵捐鐢佃剳绠″V15.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� office2016婵€娲诲伐鍏穔msv19.5.2 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
office2016婵€娲诲伐鍏穔msv19.5.2 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 杩呴浄11鏈€鏂扮増v11.3.6.1870 瀹樻柟鐗�
杩呴浄11鏈€鏂扮増v11.3.6.1870 瀹樻柟鐗� 360鍏嶈垂wifi5.3.0.5000 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
360鍏嶈垂wifi5.3.0.5000 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 360瀹夊叏娴忚鍣�2022v13.1.5188.0 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
360瀹夊叏娴忚鍣�2022v13.1.5188.0 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 閰锋垜闊充箰鐩�2022v9.1.6.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
閰锋垜闊充箰鐩�2022v9.1.6.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 鏆撮褰遍煶2021V5.81.0202.1111瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
鏆撮褰遍煶2021V5.81.0202.1111瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 蹇挱5.0姘镐笉鍗囩骇鐗�5.0.80 楠ㄥご鐗�
蹇挱5.0姘镐笉鍗囩骇鐗�5.0.80 楠ㄥご鐗� 浼橀叿2022瀹㈡埛绔疺8.0.9.11050 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
浼橀叿2022瀹㈡埛绔疺8.0.9.11050 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鐖卞鑹鸿棰慥13.1.5瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
鐖卞鑹鸿棰慥13.1.5瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� photoshop cs6 涓枃鐗�13.1.2.3 鍏嶈垂涓枃鐗�
photoshop cs6 涓枃鐗�13.1.2.3 鍏嶈垂涓枃鐗�![Autodesk 3ds Max 2012瀹樻柟绠€浣撲腑鏂囩増[32&64]](https://p.e5n.com/up/2018-9/2018921055101508.png) Autodesk 3ds Max 2012瀹樻柟绠€浣撲腑鏂囩増[32&64]
Autodesk 3ds Max 2012瀹樻柟绠€浣撲腑鏂囩増[32&64] CAD2007鍏嶈垂涓枃鐗�
CAD2007鍏嶈垂涓枃鐗� vc杩愯搴�2019鏈€鏂扮増v2019.3.2(32&64浣�)
vc杩愯搴�2019鏈€鏂扮増v2019.3.2(32&64浣�) .NET Framework 4.8瀹樻柟鐗�4.8.3646
.NET Framework 4.8瀹樻柟鐗�4.8.3646 QQ2022v9.5.6.28129 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
QQ2022v9.5.6.28129 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 寰俊鐢佃剳鐗�2022v3.5.0.44 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
寰俊鐢佃剳鐗�2022v3.5.0.44 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 鍗冪墰鍗栧宸ヤ綔骞冲彴v9.02.02N 瀹樻柟鐗�
鍗冪墰鍗栧宸ヤ綔骞冲彴v9.02.02N 瀹樻柟鐗� QT璇煶V4.6.80.18262瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
QT璇煶V4.6.80.18262瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 椋炰俊2018V6.2.0700 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
椋炰俊2018V6.2.0700 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 渚犵洍椋炶溅缃伓閮藉競
渚犵洍椋炶溅缃伓閮藉競 楠戦┈涓庣爫鏉€缁翠含寰佹湇
楠戦┈涓庣爫鏉€缁翠含寰佹湇 铏愭潃鍘熷舰2
铏愭潃鍘熷舰2 浠ユ拻鐨勭粨鍚�
浠ユ拻鐨勭粨鍚� 鏉€鎵�5璧﹀厤
鏉€鎵�5璧﹀厤 H1Z1涓枃鐗�
H1Z1涓枃鐗� 瀛ゅ矝鎯婇瓊3
瀛ゅ矝鎯婇瓊3 涓夎娲茬壒绉嶉儴闃�6鎴橀槦涔嬪垉
涓夎娲茬壒绉嶉儴闃�6鎴橀槦涔嬪垉 浣垮懡鍙敜8:鐜颁唬鎴樹簤3
浣垮懡鍙敜8:鐜颁唬鎴樹簤3 鍚堥噾瑁呭5:骞荤棝
鍚堥噾瑁呭5:骞荤棝 娆ф床鍗¤溅妯℃嫙2
娆ф床鍗¤溅妯℃嫙2 鏃嬭浆杞儙
鏃嬭浆杞儙 鏋佸搧椋炶溅18
鏋佸搧椋炶溅18 绁炲姏绉戣帋
绁炲姏绉戣帋 F1 2015
F1 2015 鎴戠殑涓栫晫1.8.2
鎴戠殑涓栫晫1.8.2 娉版媺鐟炰簹
娉版媺鐟炰簹 楗ヨ崚:娴烽毦
楗ヨ崚:娴烽毦 鏄熺晫杈瑰
鏄熺晫杈瑰 鏈€鍚庣敓杩樿€匬C鐗�
鏈€鍚庣敓杩樿€匬C鐗� 鏂囨槑5:缇庝附鏂颁笘鐣�
鏂囨槑5:缇庝附鏂颁笘鐣� 涓夊浗蹇�12濞佸姏鍔犲己鐗�
涓夊浗蹇�12濞佸姏鍔犲己鐗� 淇¢暱涔嬮噹鏈�14濞佸姏鍔犲己鐗�
淇¢暱涔嬮噹鏈�14濞佸姏鍔犲己鐗� 闃挎彁鎷�:鍏ㄩ潰鎴樹簤
闃挎彁鎷�:鍏ㄩ潰鎴樹簤 甯濆浗鏃朵唬2寰佹湇鑰�
甯濆浗鏃朵唬2寰佹湇鑰� 鏀粯瀹濋挶鍖�(Alipay)V10.2.53.7000 瀹夊崜鐗�
鏀粯瀹濋挶鍖�(Alipay)V10.2.53.7000 瀹夊崜鐗� 鐧惧害鍦板浘瀵艰埅2022V15.12.10 瀹夊崜鎵嬫満鐗�
鐧惧害鍦板浘瀵艰埅2022V15.12.10 瀹夊崜鎵嬫満鐗� 鎵嬫満娣樺疂瀹㈡埛绔痸10.8.40瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鎵嬫満娣樺疂瀹㈡埛绔痸10.8.40瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鐣呴€旂綉鎵嬫満瀹㈡埛绔痸5.6.9 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鐣呴€旂綉鎵嬫満瀹㈡埛绔痸5.6.9 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鍗冭亰鐭ヨ瘑鏈嶅姟appv4.5.1瀹樻柟鐗�
鍗冭亰鐭ヨ瘑鏈嶅姟appv4.5.1瀹樻柟鐗� p2psearcher瀹夊崜鐗�7.3 鎵嬫満鐗�
p2psearcher瀹夊崜鐗�7.3 鎵嬫満鐗� 閰风嫍闊充箰2022瀹樻柟鐗圴11.0.8 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
閰风嫍闊充箰2022瀹樻柟鐗圴11.0.8 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 鐖卞鑹烘墜鏈虹増v13.1.0
鐖卞鑹烘墜鏈虹増v13.1.0 鐧惧害褰遍煶7.13.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鐧惧害褰遍煶7.13.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 褰遍煶鍏堥攱v6.9.0 瀹夊崜鎵嬫満鐗�
褰遍煶鍏堥攱v6.9.0 瀹夊崜鎵嬫満鐗� 鑵捐鍔ㄦ极V9.11.5 瀹夊崜鐗�
鑵捐鍔ㄦ极V9.11.5 瀹夊崜鐗� 涔︽棗灏忚鍏嶈垂鐗堟湰v11.5.5.153 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
涔︽棗灏忚鍏嶈垂鐗堟湰v11.5.5.153 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 QQ闃呰鍣╝ppV7.7.1.910 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
QQ闃呰鍣╝ppV7.7.1.910 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鎳掍汉鐣呭惉鍚功appv7.1.5 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
鎳掍汉鐣呭惉鍚功appv7.1.5 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 璧风偣璇讳功app鏂扮増鏈�20227.9.186 瀹夊崜鐗�
璧风偣璇讳功app鏂扮増鏈�20227.9.186 瀹夊崜鐗� 骞冲畨璇佸埜瀹塭鐞嗚储V9.1.0.1 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
骞冲畨璇佸埜瀹塭鐞嗚储V9.1.0.1 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 娴烽€氳瘉鍒告墜鏈虹増(e娴烽€氳储)8.71 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
娴烽€氳瘉鍒告墜鏈虹増(e娴烽€氳储)8.71 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 涓滄捣璇佸埜涓滄捣鐞嗚储4.0.5 瀹夊崜鐗�
涓滄捣璇佸埜涓滄捣鐞嗚储4.0.5 瀹夊崜鐗� 涓摱璇佸埜绉诲姩鐞嗚储杞欢6.02.010 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
涓摱璇佸埜绉诲姩鐞嗚储杞欢6.02.010 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 鍗庨緳璇佸埜灏忛噾鎵嬫満鐞嗚储杞欢3.2.4 瀹夊崜鐗�
鍗庨緳璇佸埜灏忛噾鎵嬫満鐞嗚储杞欢3.2.4 瀹夊崜鐗� 绂忓缓鍐滄潙淇$敤绀炬墜鏈洪摱琛屽鎴风2.3.4 瀹夊崜鐗�
绂忓缓鍐滄潙淇$敤绀炬墜鏈洪摱琛屽鎴风2.3.4 瀹夊崜鐗� 鏄撳埗浣滆棰戝壀杈慳pp4.1.16瀹夊崜鐗�
鏄撳埗浣滆棰戝壀杈慳pp4.1.16瀹夊崜鐗� 涓浗宸ュ晢閾惰鎵嬫満閾惰appV7.0.1.2.5 瀹夊崜鐗�
涓浗宸ュ晢閾惰鎵嬫満閾惰appV7.0.1.2.5 瀹夊崜鐗� 涓浗閾惰鎵嬫満閾惰瀹㈡埛绔�7.2.5 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
涓浗閾惰鎵嬫満閾惰瀹㈡埛绔�7.2.5 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 鑵捐鐚庨奔杈句汉鎵嬫満鐗圴2.3.0.0 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
鑵捐鐚庨奔杈句汉鎵嬫満鐗圴2.3.0.0 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 鍔茶垶鍥㈠畼鏂规鐗堟墜娓竩1.2.1瀹樻柟鐗�
鍔茶垶鍥㈠畼鏂规鐗堟墜娓竩1.2.1瀹樻柟鐗� 楗ラタ椴ㄩ奔杩涘寲鏃犻檺閽荤煶鐗坴7.8.0.0瀹夊崜鐗�
楗ラタ椴ㄩ奔杩涘寲鏃犻檺閽荤煶鐗坴7.8.0.0瀹夊崜鐗� 妞嶇墿澶ф垬鍍靛案鍏ㄦ槑鏄�1.0.91 瀹夊崜鐗�
妞嶇墿澶ф垬鍍靛案鍏ㄦ槑鏄�1.0.91 瀹夊崜鐗� 鍦颁笅鍩庣獊鍑昏€卋t鐗�1.6.3 瀹樻柟鐗�
鍦颁笅鍩庣獊鍑昏€卋t鐗�1.6.3 瀹樻柟鐗� 瑁呯敳鑱旂洘1.325.157 瀹夊崜鐗�
瑁呯敳鑱旂洘1.325.157 瀹夊崜鐗� 鍦f枟澹槦鐭㈤泦缁搗4.2.1 瀹夊崜鐗�
鍦f枟澹槦鐭㈤泦缁搗4.2.1 瀹夊崜鐗� 閬ぉ3D鎵嬫父1.0.9瀹夊崜鐗�
閬ぉ3D鎵嬫父1.0.9瀹夊崜鐗� 瀹夊崜妞嶇墿澶ф垬鍍靛案2榛戞殫鏃朵唬淇敼鐗圴1.9.5 鏈€鏂扮増
瀹夊崜妞嶇墿澶ф垬鍍靛案2榛戞殫鏃朵唬淇敼鐗圴1.9.5 鏈€鏂扮増 涔辨枟瑗挎父2v1.0.150瀹夊崜鐗�
涔辨枟瑗挎父2v1.0.150瀹夊崜鐗� 淇濆崼钀濆崪3鏃犻檺閽荤煶鏈€鏂扮増v2.0.0.1 瀹夊崜鐗�
淇濆崼钀濆崪3鏃犻檺閽荤煶鏈€鏂扮増v2.0.0.1 瀹夊崜鐗� 鍙h鑻遍泟鍗曟満鐗�1.2.0 瀹夊崜鐗�
鍙h鑻遍泟鍗曟満鐗�1.2.0 瀹夊崜鐗� 灏忓皬鍐涘洟瀹夊崜鐗�2.7.4 鏃犻檺閲戝竵淇敼鐗�
灏忓皬鍐涘洟瀹夊崜鐗�2.7.4 鏃犻檺閲戝竵淇敼鐗� 鐧诲北璧涜溅2鎵嬫父1.47.1 瀹夊崜鐗�
鐧诲北璧涜溅2鎵嬫父1.47.1 瀹夊崜鐗� 涓€璧锋潵椋炶溅瀹夊崜鐗坴2.9.14 鏈€鏂扮増
涓€璧锋潵椋炶溅瀹夊崜鐗坴2.9.14 鏈€鏂扮増 璺戣窇鍗′竵杞︽墜鏈虹増瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増v1.16.2 瀹夊崜鐗�
璺戣窇鍗′竵杞︽墜鏈虹増瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増v1.16.2 瀹夊崜鐗� 鐙傞噹椋欒溅8鏋侀€熷噷浜戜慨鏀圭増(鍏嶆暟鎹寘)v4.6.0j 閲戝竵鏃犻檺鐗�
鐙傞噹椋欒溅8鏋侀€熷噷浜戜慨鏀圭増(鍏嶆暟鎹寘)v4.6.0j 閲戝竵鏃犻檺鐗� 鐧句箰鍗冪偖鎹曢奔2021鏈€鏂扮増5.78 瀹夊崜鐗�
鐧句箰鍗冪偖鎹曢奔2021鏈€鏂扮増5.78 瀹夊崜鐗� 姊﹀够鍓戣垶鑰呭彉鎬佺増1.0.1.2瀹夊崜鐗�
姊﹀够鍓戣垶鑰呭彉鎬佺増1.0.1.2瀹夊崜鐗� 浠欏浼犺ro澶嶅叴瀹夊崜鐗�1.20.3鏈€鏂扮増
浠欏浼犺ro澶嶅叴瀹夊崜鐗�1.20.3鏈€鏂扮増 姊﹀够璇涗粰鎵嬫父鐗�1.3.6 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗�
姊﹀够璇涗粰鎵嬫父鐗�1.3.6 瀹樻柟瀹夊崜鐗� 鐜嬭€呰崳鑰€V3.72.1.1 瀹夊崜鏈€鏂板畼鏂圭増
鐜嬭€呰崳鑰€V3.72.1.1 瀹夊崜鏈€鏂板畼鏂圭増 璋佸灏忚溅寮烘墜鏈虹増v1.0.49 瀹夊崜鐗�
璋佸灏忚溅寮烘墜鏈虹増v1.0.49 瀹夊崜鐗� mac纾佺洏鍒嗗尯宸ュ叿(Paragon Camptune X)V10.8.12瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
mac纾佺洏鍒嗗尯宸ュ叿(Paragon Camptune X)V10.8.12瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鑻规灉鎿嶄綔绯荤粺MACOSX 10.9.4 Mavericks瀹屽叏鍏嶈垂鐗�
鑻规灉鎿嶄綔绯荤粺MACOSX 10.9.4 Mavericks瀹屽叏鍏嶈垂鐗� Rar瑙e帇鍒╁櫒mac鐗坴1.4 瀹樻柟鍏嶈垂鐗�
Rar瑙e帇鍒╁櫒mac鐗坴1.4 瀹樻柟鍏嶈垂鐗� Mac瀹夊崜妯℃嫙鍣�(ARC Welder)v1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
Mac瀹夊崜妯℃嫙鍣�(ARC Welder)v1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 Charles for MacV3.9.3瀹樻柟鐗�
Charles for MacV3.9.3瀹樻柟鐗� 鎼滅嫍娴忚鍣╩ac鐗坴5.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
鎼滅嫍娴忚鍣╩ac鐗坴5.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 閿愭嵎瀹㈡埛绔痬ac鐗圴1.33瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
閿愭嵎瀹㈡埛绔痬ac鐗圴1.33瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 蹇墮mac鐗坴1.3.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
蹇墮mac鐗坴1.3.2 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 鏋佺偣浜旂瑪Mac鐗�7.13姝e紡鐗�
鏋佺偣浜旂瑪Mac鐗�7.13姝e紡鐗� Apple Logic Pro xV10.3.2
Apple Logic Pro xV10.3.2 Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2017 mac鐗坴11.0.0 涓枃鐗�
Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2017 mac鐗坴11.0.0 涓枃鐗� 鍗冨崈闈欏惉Mac鐗圴9.1.1 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鍗冨崈闈欏惉Mac鐗圴9.1.1 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 Mac缃戠粶鐩存挱杞欢(MacTV)v0.121 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
Mac缃戠粶鐩存挱杞欢(MacTV)v0.121 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 Adobe Fireworks CS6 Mac鐗圕S6瀹樻柟绠€浣撲腑鏂囩増
Adobe Fireworks CS6 Mac鐗圕S6瀹樻柟绠€浣撲腑鏂囩増 AutoCAD2015 mac涓枃鐗堟湰v1.0 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
AutoCAD2015 mac涓枃鐗堟湰v1.0 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� Adobe Photoshop cs6 mac鐗坴13.0.3 瀹樻柟涓枃鐗�
Adobe Photoshop cs6 mac鐗坴13.0.3 瀹樻柟涓枃鐗� Mac鐭㈤噺缁樺浘杞欢(Sketch mac)v3.3.2 涓枃鐗�
Mac鐭㈤噺缁樺浘杞欢(Sketch mac)v3.3.2 涓枃鐗� Adobe After Effects cs6 mac鐗坴1.0涓枃鐗�
Adobe After Effects cs6 mac鐗坴1.0涓枃鐗� Adobe InDesign cs6 mac1.0 瀹樻柟涓枃鐗�
Adobe InDesign cs6 mac1.0 瀹樻柟涓枃鐗�![Mac鐗堝揩鎾�1.1.26 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗圼dmg]](https://p.e5n.com/up/2014-8/201484111558.jpg) Mac鐗堝揩鎾�1.1.26 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗圼dmg]
Mac鐗堝揩鎾�1.1.26 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗圼dmg] Mac璇诲啓NTFS(Paragon NTFS for Mac)12.1.62 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
Mac璇诲啓NTFS(Paragon NTFS for Mac)12.1.62 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 杩呴浄10 for macv3.4.1.4368 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
杩呴浄10 for macv3.4.1.4368 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 Mac涓嬫渶寮哄ぇ鐨勭郴缁熸竻鐞嗗伐鍏�(CleanMyMac for mac)v3.1.1 姝e紡鐗�
Mac涓嬫渶寮哄ぇ鐨勭郴缁熸竻鐞嗗伐鍏�(CleanMyMac for mac)v3.1.1 姝e紡鐗� 鑻规灉BootCamp5.1.5640 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鑻规灉BootCamp5.1.5640 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 寰俊ipad鐗�2020v7.0.12 瀹樻柟鐗�
寰俊ipad鐗�2020v7.0.12 瀹樻柟鐗� iphone鎵嬫満qq2021v8.5.0 瀹樻柟鐗�
iphone鎵嬫満qq2021v8.5.0 瀹樻柟鐗� 鏄撲俊iOS鐗坴7.3.13 iPhone鐗�
鏄撲俊iOS鐗坴7.3.13 iPhone鐗� 闄岄檶 iphoneV8.32.4 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗�
闄岄檶 iphoneV8.32.4 瀹樻柟姝e紡鐗� 鍗冪墰 iphone鐗�9.2.5 瀹樻柟鐗�
鍗冪墰 iphone鐗�9.2.5 瀹樻柟鐗� 99涓ラ€夋渶鏂扮増V1.3.6
99涓ラ€夋渶鏂扮増V1.3.6 蹇墮iPhone鐗�5.7.3 瀹樻柟鐗�
蹇墮iPhone鐗�5.7.3 瀹樻柟鐗� 娣樺疂 for iPhonev9.5.15 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
娣樺疂 for iPhonev9.5.15 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 澧ㄨ抗澶╂皵 for iphoneV7.5.3瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増IPA
澧ㄨ抗澶╂皵 for iphoneV7.5.3瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増IPA 璋锋瓕鍦板浘iphone(Google Maps)4.54 涓枃鐗�
璋锋瓕鍦板浘iphone(Google Maps)4.54 涓枃鐗�![蹇挱鑻规灉鐗圴3.3.35 瀹樻柟鐗圼ipa]](https://p.e5n.com/up/2011-12/20111215155620.gif) 蹇挱鑻规灉鐗圴3.3.35 瀹樻柟鐗圼ipa]
蹇挱鑻规灉鐗圴3.3.35 瀹樻柟鐗圼ipa] 鍚夊悏褰遍煶鎾斁鍣╥os鐗�1.0.1017 鑻规灉ipad鐗�
鍚夊悏褰遍煶鎾斁鍣╥os鐗�1.0.1017 鑻规灉ipad鐗� 褰遍煶鍏堥攱鎾斁鍣╥os鐗�2.8.0 瀹樻柟鐗�
褰遍煶鍏堥攱鎾斁鍣╥os鐗�2.8.0 瀹樻柟鐗� 鏂楅奔鐩存挱瀹㈡埛绔痠os鐗�7.0.1 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鏂楅奔鐩存挱瀹㈡埛绔痠os鐗�7.0.1 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 閰风嫍闊充箰 for iPhonev10.9.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
閰风嫍闊充箰 for iPhonev10.9.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 How old do I look ios鐗�1.02 瀹樻柟鐗�
How old do I look ios鐗�1.02 瀹樻柟鐗� 缇庡浘绉€绉€iPhone鐗圴8.6.62 鏈€鏂版寮忕増
缇庡浘绉€绉€iPhone鐗圴8.6.62 鏈€鏂版寮忕増 姘村嵃闃熼暱鑻规灉鐗坴1.0.0
姘村嵃闃熼暱鑻规灉鐗坴1.0.0 澶╁ぉp鍥緄pad鐗�5.7.4 瀹樻柟鐗�
澶╁ぉp鍥緄pad鐗�5.7.4 瀹樻柟鐗� 蹇墜ios鐗圴9.6.30 瀹樻柟鐗�
蹇墜ios鐗圴9.6.30 瀹樻柟鐗� 鑳屽寘鍦板浘ios鐗�1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鑳屽寘鍦板浘ios鐗�1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 鎵嬫満瀹夊叏鍔╂墜鑻规灉鐗坴1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増
鎵嬫満瀹夊叏鍔╂墜鑻规灉鐗坴1.0 瀹樻柟鏈€鏂扮増 UC娴忚鍣╒113.5.5.1555涓枃鐗�
UC娴忚鍣╒113.5.5.1555涓枃鐗� 360娴忚鍣℉D for iPadV4.1.3 姝e紡鐗�
360娴忚鍣℉D for iPadV4.1.3 姝e紡鐗� iPhone鎵嬫満QQ娴忚鍣╒8.9.1 瀹樻柟鐗�
iPhone鎵嬫満QQ娴忚鍣╒8.9.1 瀹樻柟鐗�
 喜欢
喜欢  顶
顶 难过
难过 囧
囧 围观
围观 无聊
无聊



